An argenx representative will contact you soon, so keep an eye on your inbox.
gMG: A chronic, debilitating, IgG-mediated autoimmune disease1-3
In gMG, pathogenic IgG autoantibodies attack key components of the NMJ. This can cause4,5:
gMG=generalized myasthenia gravis; IgG=immunoglobulin G; NMJ=neuromuscular junction.
IgG autoantibodies are a key driver of gMG5-9*
IgG autoantibodies target multiple components of the NMJ, including AChR, MuSK, and LRP4.5
- 85% of patients have autoantibodies against AChR3
- ~5% of patients have autoantibodies against MuSK1,3
- ~1-~3% of patients have autoantibodies against LRP41
- ~10% of patients are seronegative with no identifiable autoantibodies1
- <p><b>1. Functional blockade</b></p>
- <p>2. Cross-linking</p>
- <p><b>3. Complement activation</b></p>
KEY
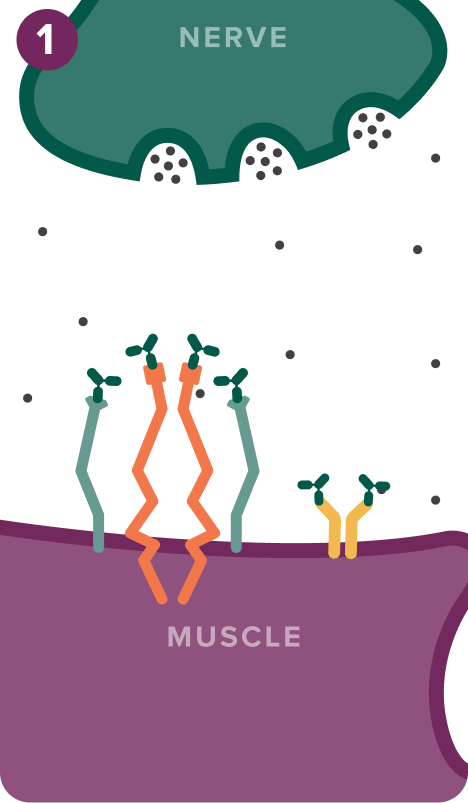
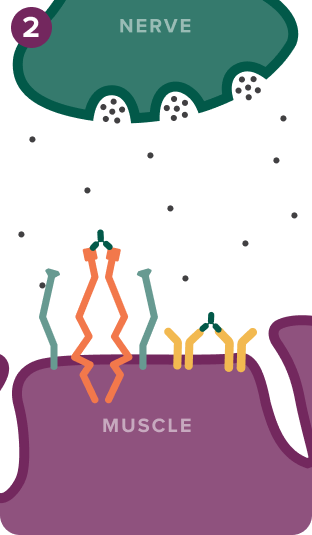
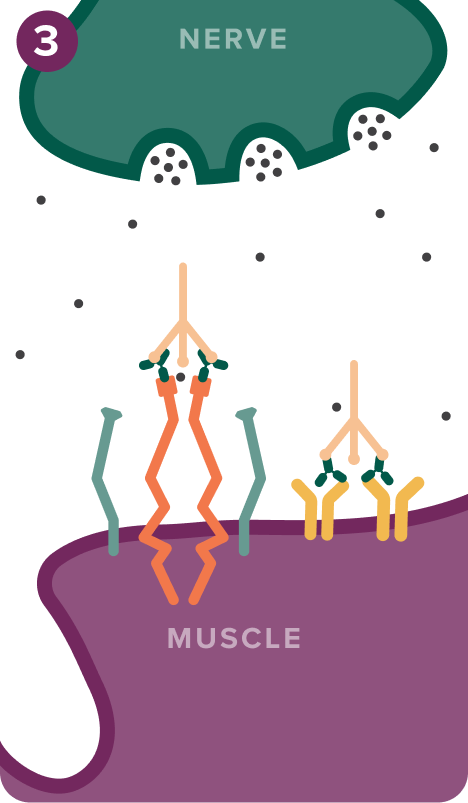
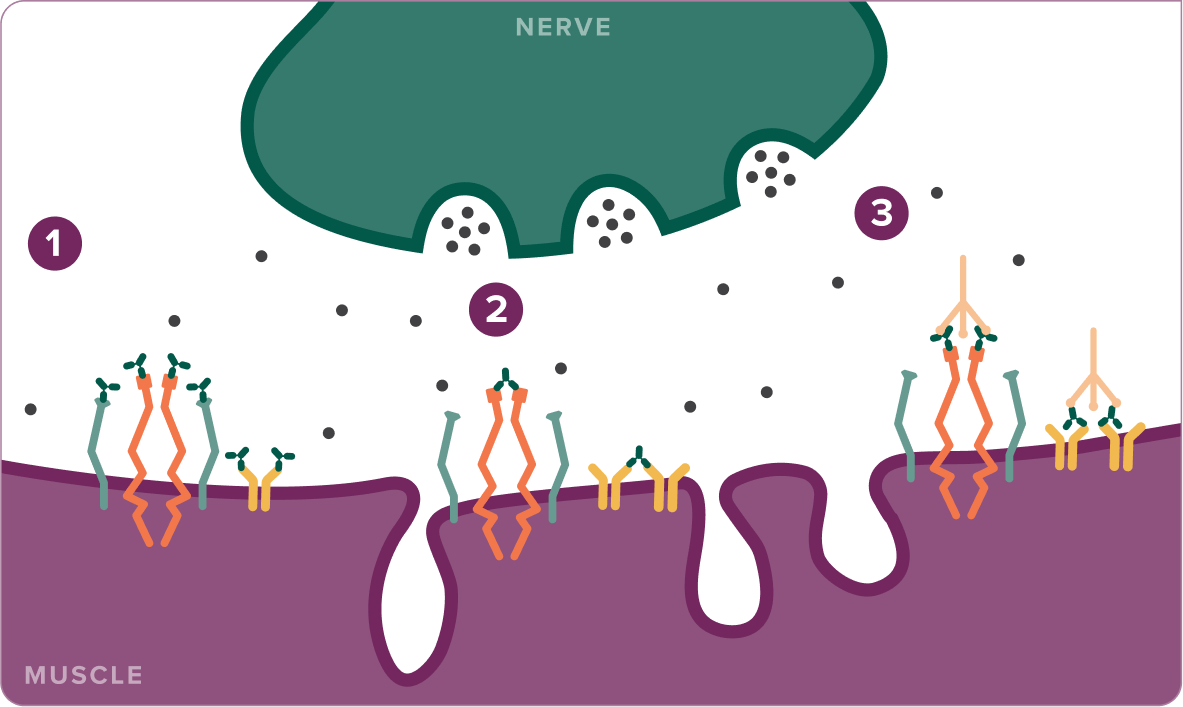
IgG autoantibodies disrupt neurotransmission in 3 ways:
1. Functional blockade
IgG autoantibodies bind to AChR, MuSK, and LRP4 receptors, creating a functional blockade. Acetylcholine is unable to bind to AChR, disrupting the interaction between MuSK and LRP4, which decreases the clustering of AChR5-10
2. Cross-linking
IgG autoantibodies cross-link AChR and LRP4 receptors, leading to internalization and degradation5-9
3. Complement activation
IgG autoantibodies activate the autoantibody dependent complement system (C1 complex)5-9
*AChR autoantibodies are a subtype of IgG autoantibodies.5,8
AChR=acetylcholine receptor; C1=complement component 1; gMG=generalized myasthenia gravis; IgG=immunoglobulin G; LRP4=low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 4; MuSK=muscle-specific tyrosine kinase; NMJ=neuromuscular junction.
FcRn plays a critical role in IgG regulation3,6,7,9,11,12
FcRn plays a critical role in enabling damage at the NMJ by:
- Binding IgG antibodies, including autoantibodies
- Rescuing them from lysosomal degradation
- Recycling them back into circulation
In doing so, FcRn helps maintain high levels of circulating IgG antibodies, including IgG autoantibodies.
FcRn=neonatal Fc receptor; IgG=immunoglobulin G; NMJ=neuromuscular junction.
This recycling process prolongs the half-life of IgG antibodies and maintains high concentrations of IgG autoantibodies that attack vital components of the NMJ.
Explore resources to help explain gMG to your patients
References: 1. Gilhus NE. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(26):2570-2581. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1602678 2. Rødgaard A et al. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987;67(1):82-88. 3. Behin A, Le Panse R. J Neuromuscul Dis. 2018;5(3):265-277. doi:10.3233/JND-170294 4. Twork S et al. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2010;8:129. doi:10.1186/1477-7525-8-129 5. Gilhus NE et al. Nat Rev Neurol. 2016;12(5):259-268. doi:10.1038/nrneurol.2016.44 6. Roopenian DC, Akilesh S. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7(9):715-725. doi:10.1038/nri2155 7. Ward ES, Ober RJ. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2018;39(10):892-904. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2018.07.007 8. Huijbers MG et al. J Intern Med. 2014;275(1):12-26. doi:10.1111/joim.12163 9. Mantegazza R et al. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2011;7:151-160. doi:10.2147/NDT.S8915 10. Conti-Fine BM et al. J Clin Invest. 2006;116(11):2843-2854. doi:10.1172/JCI29894 11. Zhu LN et al. Neural Regen Res. 2023;18(8):1637-1644. doi:10.4103/1673-5374.363824 12. Ulrichts P et al. J Clin Invest. 2018;128(10):4372-4386. doi:10.1172/JCI97911
We’ll be in touch!
Thank you for signing up!
We’re looking forward to sharing information about innovations in gMG with you. Keep an eye on your inbox for important updates on Raising the Bar in gMG.
gMG=generalized myasthenia gravis.